Qingxiu Mountain
1. Introduction
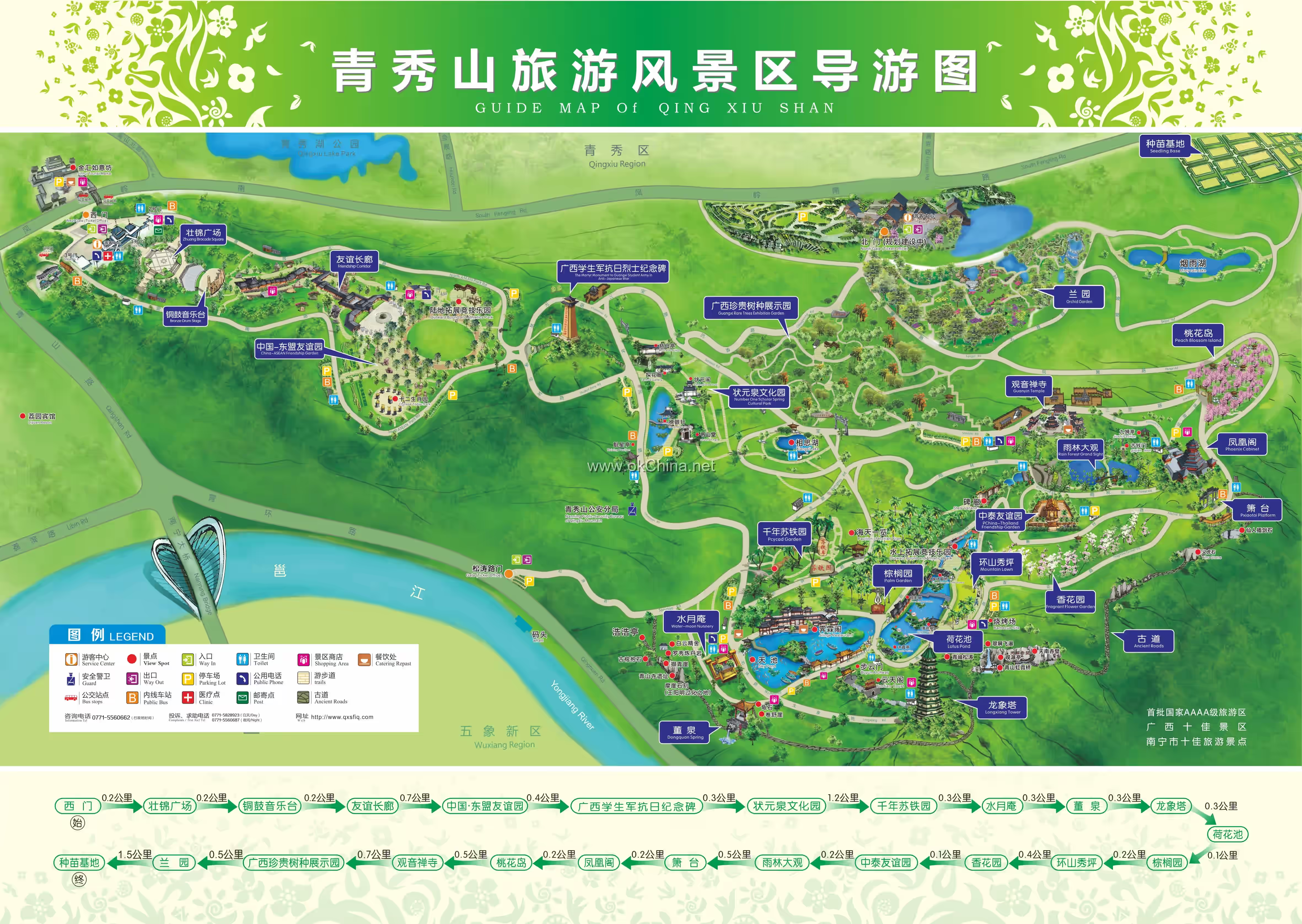
Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area, located in Qingxiu District, Nanning City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, is one of the most representative natural landscapes and tourist destinations in Nanning. Renowned for its beautiful mountain scenery, lush vegetation, and long history, it is hailed as "Nanning's Green Lung" and the "City's Back Garden." The scenic area covers a total area of approximately 13.54 square kilometers, integrating natural scenery, cultural landscapes, religious culture, and leisure entertainment. It is a National Scenic Area and a National AAAAA Tourist Attraction.
The history of Qingxiu Mountain dates back to the Tang Dynasty, spanning over a thousand years. The mountain is home to numerous historical relics and cultural sites, such as the Longxiang Pagoda from the Tang Dynasty, the Guanyin Zen Temple from the Ming Dynasty, and the Dong Spring from the Qing Dynasty. The Longxiang Pagoda is the iconic structure of Qingxiu Mountain. This nine-story pagoda offers a panoramic view of Nanning City from its top, providing a refreshing and expansive vista. The Guanyin Zen Temple is a famous Buddhist sanctuary in Guangxi, attracting a large number of tourists and devotees each year with its thriving incense offerings.
2. Geographical Environment
2.1 Location and Territory
Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area is located at No. 6 Fengling South Road, Qingxiu District, Nanning City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Situated along the Yongjiang River, it stretches from Qingshan Road in the west to the ASEAN Business District in the north, with the Yongjiang River bordering its southern and eastern sides. The area covers 13.54 square kilometers.
2.2 Topography and Landforms
Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area is surrounded by hilly terrain, with higher elevations in the north and lower in the south. It features over 200 hills and peaks, with elevations ranging from 63.9 to 288.3 meters. The highest point is Fenghuang (Phoenix) Ridge.
2.3 Climate
Qingxiu District, Nanning City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, where the scenic area is located, lies south of the Tropic of Cancer. Influenced by maritime climate, it experiences a subtropical monsoon climate characterized by abundant sunshine, ample rainfall, little frost, and no snow. The annual average temperature is 21.7°C.
3. Main Attractions
3.1 Longxiang Pagoda
Longxiang Pagoda, also known as Qingshan Pagoda, is the landmark of Qingxiu Mountain. It stands atop Qingxiu Mountain by the Yongjiang River in Nanning, the capital of Guangxi.
The pagoda was originally built in the 47th year of the Wanli era of the Ming Dynasty (1619) by Xiao Yunju, a native of Nanning who achieved the Jinshi degree and served as Vice Minister of Personnel in the imperial court. The original pagoda was over 30 meters tall but later lost two stories to a lightning strike. In August 1937, fearing the pagoda might become a target for Japanese bombers, the local government ordered its demolition. From December 1985 to September 1987, the municipal government reconstructed the Longxiang Pagoda in the Ming Dynasty architectural style. The new pagoda stands 52.35 meters high with a base diameter of 12 meters. It is an octagonal, nine-story structure with green glazed tiles on the roof. Each upturned eave corner hangs a bronze bell, totaling 72 bells. Inside, a 207-step spiral staircase allows visitors to ascend from the first to the ninth floor, where they can enjoy a panoramic view of Nanning City.
Longxiang Pagoda is located on Fengchi (Phoenix Wing) Ridge of Qingxiu Mountain. Legend has it that Xiao Yunju's ancestral tomb was situated in a geomantically auspicious site known as "Phoenix Playing with Peony," which supposedly brought him great fortune and high office. However, a feng shui master warned that a phoenix could fly away. To ensure his descendants would continue to hold high office, Xiao Yunju needed to keep the phoenix grounded by pinning down its wings. Believing this, Xiao funded the construction of Longxiang Pagoda atop Fengchi Ridge, hoping the pagoda would weigh down the phoenix's wings. Another legend suggests that officials and wealthy individuals of the time were superstitious about feng shui. It was believed that in counties and prefectures with rivers, pagodas should be built to "lock the water mouth," preventing wealth from flowing away and ensuring local prosperity. Xiao Yunju built the pagoda both for his own benefit and for Nanning, receiving support from the local prefect.
In August 1937, fearing the pagoda might become a target for Japanese bombers, the local government ordered its demolition. From December 1985 to September 1987, the municipal government reconstructed the Longxiang Pagoda in the Ming Dynasty architectural style. The new pagoda stands 52.35 meters high with a base diameter of 12 meters. It is an octagonal, nine-story structure with green glazed tiles on the roof. Each upturned eave corner hangs a bronze bell, totaling 72 bells. Inside, a 207-step spiral staircase allows visitors to ascend from the first to the ninth floor, where they can enjoy a panoramic view of Nanning City.
3.2 Millennium Cycad Garden
The Millennium Cycad Garden within Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area covers over 100 mu (approximately 6.67 hectares) and houses nearly a hundred cycads over a thousand years old. The oldest, known as the "Cycad King," is over 1,360 years old. The garden has collected more than 50 species of cycads, totaling over ten thousand plants. It is one of China's largest ex-situ conservation and breeding bases for species such as Cycas pectinata, Cycas debaoensis, Cycas bifida, and Cycas sexseminifera.
3.3 Orchid Garden
The Orchid Garden is located southeast of the North Gate area of Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area, covering a total area of 320 mu (approximately 21.33 hectares). The first phase, spanning 150 mu, focuses on "exotic orchid landscaping." Based on the ecological habits of various orchids, they are naturally planted among trees, in rock crevices, and along gullies, creating scenic spots like "Stone-Embraced Cascading Waterfall," "Sky Garden," "Emerald Screen and Orchid Fragrance," "Brilliant Orchid Fields," "Ancient Pottery and Orchid Charm," and "Slipper Orchid Waterfall." This phase features 363 orchid species with a total of over 300,000 plants. The second phase, covering 170 mu, centers on "medicinal orchid wellness" and "Chinese orchid culture." It incorporates classical garden structures like pavilions, corridors, and verandas into the landscape, enhancing the garden's cultural depth, increasing orchid varieties, and showcasing the medicinal value of orchids. Designed in a natural and rustic style, it aims to be a specialized outdoor orchid garden and is also the largest natural ecological orchid garden in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region and even China.
3.4 Cherry Blossom Garden
Located on the eastern side of Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area, the Cherry Blossom Garden is themed "Poetic and Picturesque, Romantic Garden." It explores Chinese cherry blossom culture and love stories, creating romantic cherry blossom landscapes. Based on the terrain, it is divided into four scenic areas: Dense Forest Flower Sea, Sparse Forest Flower Lawn, Cherry Grove Flower Slope, and Cherry Blossom Riverside. The garden features nearly 6,000 cherry trees of seven different varieties: China Red, Guangzhou Cherry, Xiaoqiao, Crimson Fujian Mountain Cherry, Pink Fujian Mountain Cherry, Bellflower Cherry, and Mountain Cherry. It is designed as a "Cherry Blossom Love Theme Park" with观赏性 (ornamental value), 可参与性 (interactivity), 文化性 (cultural significance), and 科普性 (educational value).
3.5 Friendship Long Corridor
The Friendship Long Corridor is situated between the Zhuangjin Square and the ASEAN Friendship Garden within Qingxiu Mountain Tourist Scenic Area, stretching 618 meters long. Modeled after the covered wind-and-rain bridges of the Dong ethnic group in Guangxi and incorporating Lingnan garden architectural styles, the corridor was constructed without a single nail or rivet, using mortise and tenon joints of Korean pine, showcasing the superb architectural skills of the Dong people. The Friendship Long Corridor integrates bridge, corridor, pavilion, and tower elements, serving both as a scenic attraction and a resting place. It displays photographic works depicting the production and daily life of Guangxi's various ethnic groups, as well as pictures and materials showcasing representative architecture, clothing, and cuisine of ASEAN countries.
3.6 Rainforest Grand View
The Rainforest Grand View within Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area was completed in 1998, covering over 500 mu (approximately 33.33 hectares). It boasts a rich variety of species and layered vegetation, hosting over 200 families, 2,500 species, and more than 3 million plants. It features characteristic rainforest plants like Dracontomelon duperreanum, Arenga pinnata, and Ficus racemosa, as well as over 180 nationally protected plants such as Parashorea chinensis, Cyathea spinulosa, and Dalbergia odorifera. The negative oxygen ion concentration here reaches 20,000 per cubic centimeter.
3.7 Guanyin Zen Temple
The Guanyin Zen Temple within Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area was first built during the Northern Song Dynasty, boasting a history of over a thousand years. It covers an area of 15 mu (approximately 1 hectare) and includes over ten Buddhist halls, such as the Mahavira Hall, Reclining Buddha Hall, Dharma Protector Hall, Prajna Hall, and Sangharama Hall.
3.8 Monument to the Guangxi Anti-Japanese Student Army
The Monument to the Guangxi Anti-Japanese Student Army within Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area was built in December 2001. Standing 20 meters tall and constructed of granite, the monument features a roof of green glazed tiles with upturned eaves and double-layered roofs, presenting a majestic and grand appearance. The monument commemorates the anti-Japanese history of the Guangxi Student Army: during the occupation of Nanning in 1939, these seemingly frail scholars participated in 978 battles against the enemy, fighting bravely, with over ten sacrificing their lives. It has been designated as a Guangxi Patriotic Education Base.
3.9 Peach Blossom Island
Peach Blossom Island is located in the northeastern part of the core scenic area of Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area, covering approximately 200 mu (about 13.33 hectares). It is named for its island-like formation surrounded by valleys on three sides and often shrouded in mist, resembling a fairyland. The island is planted with tens of thousands of peach trees of over ten varieties, including hairy peach, crimson peach, fragrant peach, human-face peach, sun-moon peach, and pink jade peach.
3.10 Guangxi Precious Tree Species Display Garden
The Guangxi Precious Tree Species Display Garden within Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area covers approximately 300 mu (about 20 hectares). It focuses on collecting, displaying, protecting, and breeding precious native tree species of Guangxi, serving as a specialized botanical garden integrating科普教育 (science education) and旅游观光 (tourism). The garden features over 1,000 large-scale precious trees with high ornamental value, strong趣味性 (interest), and rich cultural内涵 (connotations). These include nationally first-class protected plants like Camellia nitidissima, Parashorea chinensis, and Taxus chinensis, as well as second-class protected plants like Burretiodendron hsienmu, Dalbergia odorifera (Huanghuali), and Aquilaria sinensis (Agarwood).
3.11 Osmanthus Garden
The Osmanthus Garden within Qingxiu Mountain Scenic Tourist Area is known as the "Valley of Fragrance" in downtown Nanning and embodies the spirit of Guangxi (Bagui). The Fragrant Valley Osmanthus Garden covers over 240 mu (approximately 16 hectares) and contains approximately ten thousand osmanthus trees, primarily from four major categories: Golden Osmanthus, Silver Osmanthus, Orange Osmanthus, and Four-Season Osmanthus, totaling over 40 varieties. It also features tens of thousands of other fragrant plants like magnolia, banana shrub (Michelia figo), and aglaia. It is an ecological specialized garden characterized by osmanthus landscaping, the display of osmanthus varieties, and osmanthus-themed culture.## 4. Cultural Resources
4.1 Historical Evolution
During the Eastern Jin Dynasty, Luo Xiu, a disciple of Ge Hong, was already practicing alchemy in the "Danyan" cave on Xieqing Cliff. After the Tang Dynasty, temples and monasteries were gradually built on Qingxiu Mountain.
In the 31st year of the Ming Jiajing era (1552), Fang Yu, the prefect of Nanning, and Xu Pu, the military commander of the Zuojiang region, built the "Baiyun Jingshe" (White Cloud Retreat) and two pavilions, the "Dongxu Pavilion" and the "Dongquan Pavilion," for Dong Chuance, a demoted supervising censor from the Ministry of Justice who had been sent to Yong (present-day Nanning).
In the 40th year of the Ming Jiajing era (1561), Ouyang Yu, a disciple of Wang Yangming and a military commander of the Zuojiang region, inscribed "The Land Where Master Yangming Passed and Transformed" on Xieqing Cliff halfway up the mountain.
From 1952 to 1960, Qingxiu Mountain was incorporated into the Nanning Farm, serving as its First Production Team. It was later renamed the Nanning Horticultural Production Experimental Farm.
In 1960, the First Production Team of Qingxiu Mountain was transferred to the management of the Foreign Affairs Office of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region.
In March 1965, the Foreign Affairs Office of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region transferred Qingxiu Mountain to the management of the Party Committee of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, renaming it the "Directly Affiliated Organs Forest Farm of the Autonomous Region."
In 1970, the Revolutionary Committee of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region delegated the management of Qingxiu Mountain to the Revolutionary Committee of Nanning City, after which it was renamed the "Nanning Qingxiu Mountain Forest Farm."
In 1986, the People's Government of Nanning City allocated funds to begin the reconstruction of the Nanning Qingxiu Mountain Scenic and Historic Interest Area.
In October 1987, the Nanning Qingxiu Mountain Scenic and Historic Interest Area was officially opened to the public.
On November 30, 2012, construction began on the West Zone parking lot of the Nanning Qingxiu Mountain Scenic and Historic Interest Area; on December 22 of the same year, maintenance work started on the main road of the scenic area.
On March 18, 2013, the maintenance of the main road in the scenic area was completed; on July 1 of the same year, the West Zone parking lot was completed.
On February 17, 2014, construction began on the East Zone parking lot of the Nanning Qingxiu Mountain Scenic and Historic Interest Area.
On April 1, 2015, construction began on the West Gate of the Nanning Qingxiu Mountain Scenic and Historic Interest Area; on May 15 of the same year, the West Gate was completed.
4.2 Cultural Activities
From January 30 to February 28, 2022, the Nanning Qingxiu Mountain Scenic and Historic Interest Area held a Spring Festival Poetry Competition.
On November 15, 2023, the closing ceremony of the First National Student (Youth) Games was held at the Tonggu Music Stage of the West Gate of Qingxiu Mountain in Nanning, Guangxi. From November 25 to December 24 of the same year, the 8th Qingxiu Mountain Chrysanthemum Exhibition was held at the ASEAN Friendship Garden.











Comments
Post a Comment