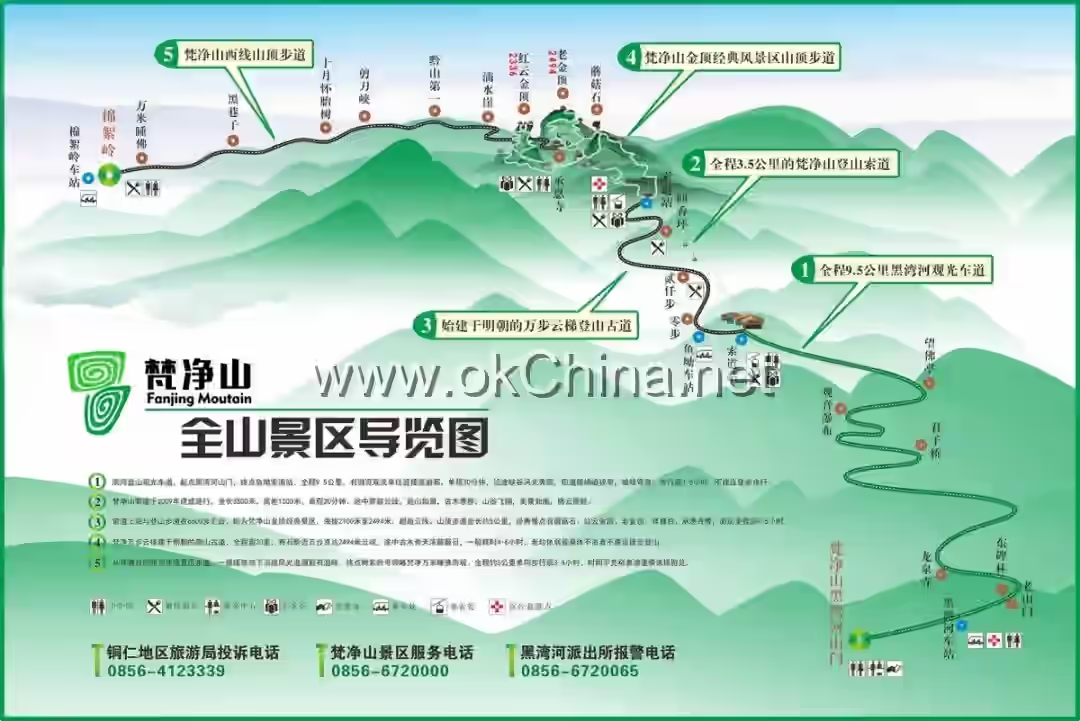
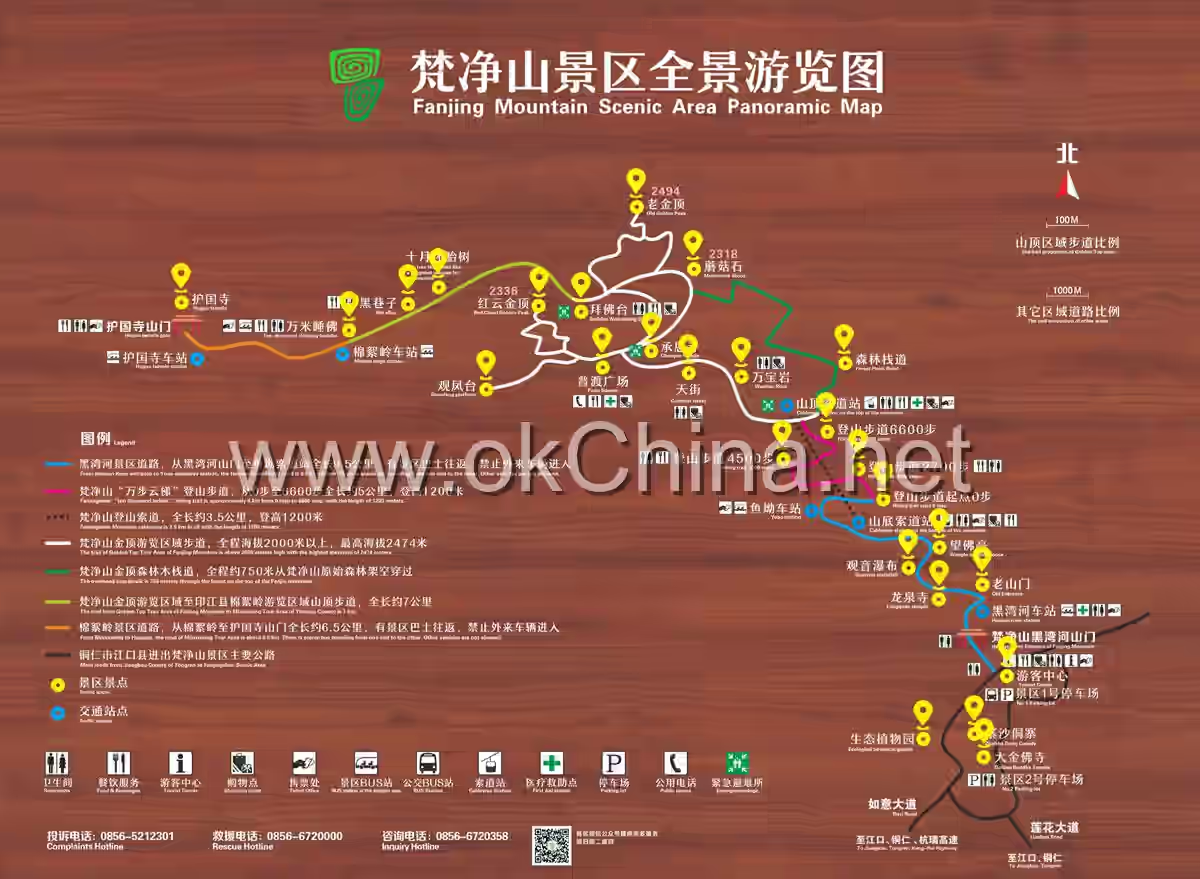
Mount Fanjing Scenic Area in Jiangkou County, Tongren City
1. Introduction
Mount Fanjing, the main peak of the Wuling Mountain Range, stands at an elevation of 2,572 meters. It is located at the junction of Jiangkou, Yinjiang, and Songtao counties in Tongren City, Guizhou Province. The total area is 775.14 square kilometers, comprising a heritage site of 402.75 square kilometers and a buffer zone of 372.39 square kilometers.
Mount Fanjing is one of the earliest areas in southern China to have uplifted from the ocean to become land, dating back approximately 1.4 billion years. It lies within the subtropical humid monsoon climate zone, preserving a pristine subtropical ecosystem and harboring ancient and rare species from 70 million to 2 million years ago. It is home to over 7,100 species of wild flora and fauna and serves as the sole habitat for the Guizhou snub-nosed monkey.
Mount Fanjing is a culturally renowned mountain in southwestern China with a history spanning over 2,000 years. As early as the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods, it belonged to the "Qianzhong Territory" of the Chu State. During the Qin Dynasty, it was part of the "Qianzhong Commandery," and in the Han Dynasty, it fell under the "Wuling Commandery." Throughout history, it has been revered as a sacred mountain by the "Wuling Man" ethnic groups. Buddhism was introduced to Mount Fanjing during the Tang Dynasty and flourished in the Ming Dynasty. The "Imperial Stele" erected during the Wanli reign of the Ming Dynasty praised Mount Fanjing as "the ancestor of all famous mountains under heaven, standing firm between heaven and earth, unparalleled from ancient times to the present."
2. Geographical Environment
2.1 Formation and Evolution
Mount Fanjing is one of the earliest areas in southern China to have uplifted from the ocean to become land, dating back approximately 1.4 billion years. The main body of metamorphic rock in the Mount Fanjing block formed about 1 billion years ago during the Fanjing-Wuling orogeny. The Himalayan orogeny gradually eroded the surrounding karst landscapes, exposing the metamorphic rocks and forming a dome-shaped natural island with radial river systems. Subsequent neotectonic movements ultimately elevated Mount Fanjing majestically above the surrounding karst region, creating a dome-shaped metamorphic rock island encircled by karst low hills and mountains. The area continues to undergo intense erosion and dissection, resulting in a striking contrast between the core area and the surrounding landscapes at the base, on the slopes, and on the summit.
2.2 Climate
The Mount Fanjing region is influenced by the Southeast Asia-Pacific monsoon and belongs to the subtropical humid monsoon climate zone. The summer is significantly affected by the southeastern maritime monsoon, while the winter is generally less impacted by cold waves. The annual average temperature ranges from 13.1°C to 14.7°C. The hottest month (July) averages 25.3°C, and the coldest month (February) averages 2°C, with temperatures decreasing as elevation increases. The annual frost-free period lasts 270–278 days, with annual sunshine hours between 900 and 1,170. Annual precipitation ranges from 1,100 to 2,600 millimeters, concentrated mainly from May to October. The average relative humidity is 80%. Based on thermal zones, there is a distinct vertical zonation from the foot to the summit: central subtropical, northern subtropical, southern temperate, and central temperate zones. The overall climate is characterized by mild temperatures, abundant sunlight, plentiful rainfall, and the absence of extreme cold or heat.
2.3 Resource Status
2.3.1 Plant Resources
Mount Fanjing has 4.2 square kilometers of primary forest and serves as a convergence point for various floristic geographical components. It is rich in plant species and represents a typical preservation site for primary montane vegetation in the central subtropical zone of western China. The area hosts over 2,000 plant species, including more than 1,000 species of higher plants. Among them, 21 species are under national key protection, such as the dove tree (Davidia involucrata), and large areas of dove tree distribution have been discovered. It is a rare gene pool for biological resources globally.
From the foothills at around 500 meters to the 1,300–1,400 meter zone, the dominant vegetation is the zonal evergreen broad-leaved forest, which represents the essence of Mount Fanjing's forests. Many areas remain in a primary forest state, with dense stands, dim understories, and numerous rare organisms. Above Yuao, the 1,400–1,900 meter zone is an evergreen-deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest belt, and the 1,900–2,100 meter zone is a deciduous broad-leaved forest belt. Mount Fanjing features many large trees with thick trunks, some exceeding 1 meter in diameter. Of the 15 global floristic geographical components, 13 are found on Mount Fanjing.
2.3.2 Animal Resources
Mount Fanjing is home to 2,767 animal species, including 382 vertebrate species. Among them, 14 species are protected wildlife, such as the Guizhou snub-nosed monkey (a first-class nationally protected animal, known as the "Spirit of Mount Fanjing" and the "Earth's Only Child," with about 700 individuals remaining, found only on Mount Fanjing in the Wuling Mountain Range of Guizhou), the Assamese macaque, rhesus macaque, clouded leopard, forest musk deer, tufted deer, serow, Chinese pangolin, mandarin duck, Temminck's tragopan, golden pheasant, Reeves's pheasant, and the Chinese giant salamander (the world's largest and most precious extant amphibian). Mount Fanjing is the exclusive distribution area for the Guizhou snub-nosed monkey.
2.3.3 Tourism Resources
Primordial wilderness characterizes the landscape of Mount Fanjing, featuring majestic mountains, layered ridges, crisscrossing streams, and cascading waterfalls. Its iconic attractions include: Red Cloud Golden Summit, Moon Mirror Mountain, Ten-Thousand-Meter Sleeping Buddha, Mushroom Stone, Ten-Thousand-Volume Scriptures, Nine Dragon Pool, and Phoenix Mountain.
3. Main Attractions
Mount Fanjing is the main peak of the Wuling Mountain Range, which is the eastern extension of the Yunwu Mountain branch of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. It trends northeast and is distributed across northwestern Hunan, with elevations mostly between 800 and 1,200 meters. Over 200 peaks exceed 1,000 meters in elevation. The northern branch of the range, distributed along the Hunan-Sichuan-Hubei border, includes Bamian Mountain, Badagong Mountain, Qinglong Mountain, Dongshan Peak, and Huping Mountain. The central branch, north of the main stream of the Lishui River, includes Tianxing Mountain, Hongxing Mountain, Chaotian Pass, Zhangjiajie, and Baiyun Mountain. The southern branch extends from Guizhou Province into Hunan, including La'er Mountain, Yangfeng Mountain, Tianmen Mountain, Dalong Mountain, and Liutai Mountain. All three branches eventually disappear into the Dongting Lake Plain.
3.1 Phoenix Mountain
Phoenix Mountain is the main peak of Mount Fanjing, with an elevation of 2,572 meters. It resembles the backbone of Mount Fanjing, towering into the clouds. Its massive and expansive form, with undulating peaks emerging intermittently from the mist, appears like a slumbering dragon, majestic and mysterious.
Climbing Phoenix Mountain is a journey of self-challenge and breathtaking scenery. The rugged and steep mountain path is lined with bizarre rocks—some resembling a fairy pointing the way, others like a divine turtle exploring the sea—adding fun and surprise to the arduous ascent. As elevation increases, the vegetation undergoes fascinating changes, transitioning from dense broad-leaved forests to coniferous forests and then to alpine meadows, as if traversing a green tunnel through time.
When you finally stand atop the summit after great effort, a sense of conquering joy and awe arises naturally. Gazing into the distance, continuous mountain ranges lie prostrate beneath your feet, while sea-like clouds surge and roll between the peaks, turbulent as waves. At sunrise or sunset, golden sunlight bathes the mountains and clouds, painting the entire world into a brilliant, dreamlike canvas that makes one marvel at nature's exquisite craftsmanship and infinite charm. Phoenix Mountain is not merely a peak; it is a sacred land for the brave seeking magnificence and freedom, awaiting you to unveil its mysterious and enchanting veil.
3.2 Old Golden Summit
The Old Golden Summit, with an elevation of 2,493 meters, is the second-highest peak of Mount Fanjing. It is also known as "Moon Mirror Mountain" because images of Maitreya Buddha preaching to sentient beings often appear on its rock walls under moonlight. The Old Golden Summit houses the Lamp-Lighting Hall, dedicated to Dipamkara Buddha, one of the Buddhas of the Past. When this Buddha was born, light illuminated all directions, rendering the sun, moon, and fire pearls useless. The rocks here take various forms, with the Mushroom Stone being a unique wonder. Its top-heavy, bottom-light shape seems precarious yet has stood firm for millions of years through wind, frost, rain, and snow, becoming a symbol of Mount Fanjing's resilience. The "Seal of Heaven Overturned" resembles a giant seal descending from the sky, standing atop the summit as if bearing a mysterious decree between heaven and earth. The Old Golden Summit's terrain is steep and perilous; climbing requires using both hands and feet, but the scenery along the way makes the effort absolutely worthwhile.
Ascending along the winding mountain path, you are surrounded by lush primary forests where rare flora and fauna thrive in this pristine land. Upon reaching the summit, the view suddenly opens up, revealing continuous mountain ranges and dense forests stretching as far as the eye can see. The refreshing breeze seems capable of blowing away all worldly troubles.
In terms of religious culture, the Old Golden Summit has been a sacred pilgrimage site for numerous devotees since ancient times. Ancient temple structures are scattered across the mountaintop, with morning bells and evening drums echoing through the valleys, adding solemnity and sanctity to this ethereal place. Here, you can not only experience the magical charm of nature but also immerse yourself in a rich religious atmosphere, undergoing a profound spiritual cleansing and enlightenment, and comprehending the true essence of harmonious coexistence between humans and nature, and between humans and faith.
3.3 New Golden Summit
The New Golden Summit, with an elevation of 2,336 meters and a vertical drop of about 100 meters, is the most perilous among the three golden summits. It is often surrounded by red clouds and auspicious mists in the morning, hence also called the Red Cloud Golden Summit. Its homophonic name "Hongyun Jinding" carries the寓意 of "good fortune arriving." The upper part of the New Golden Summit is split into two isolated peaks by the "Golden Knife Gorge"—the southern peak houses the Sakyamuni Hall, dedicated to Sakyamuni Buddha, while the northern peak houses the Maitreya Hall, dedicated to Maitreya Buddha. They are connected by a sky bridge, resembling a flying dragon. Viewed from different angles, the Red Cloud Golden Summit appears either like Buddha's two fingers in a Zen gesture or a totem of life, earning it the title "The First Peak Under Heaven."
3.4 Huguo Temple
Throughout history, numerous temples have been built on Mount Fanjing, totaling hundreds of large and small temples. Among them, the "Four Imperial Temples" and the "Forty-Eight Subsidiary Temples" are the most famous. Huguo Temple, one of the Four Imperial Temples, covers an area of 3,000 square meters, with temple properties extending over 30 li in the surrounding area.
The Sakyamuni Hall and Maitreya Hall are located on the Golden Summit. Built during the Ming Dynasty, the Sakyamuni Hall is on the left, the Maitreya Hall on the right, with the Golden Knife Gorge in between. A sky bridge spans the gorge to connect the two halls. Behind each hall stands a massive rock: one called the "Sutra-Drying Platform" and the other the "Dharma-Expounding Platform."
3.5 Chengen TempleThe Chengen Temple is situated at the summit of Mount Fanjing, overlooking a deep valley over 1,000 meters below. Gazing into the distance, one can take in the vast expanse of clouds and scenery spanning hundreds of miles, creating a truly magnificent view. Chengen Temple (commonly known as the Upper Tea Hall) is located to the left of the Golden Summit. Its main hall consists of three bays, with the inscription "Imperially Bestowed Chengen Temple" carved in intaglio on the lintel. There are eight side halls on both flanks, though only remnants of some walls remain. The total built-up area covers 1,250 square meters. Zhenguo Temple (commonly known as the Lower Tea Hall) is situated below Chengen Temple. It was initially built during the Ming Dynasty but collapsed in the 1950s. There were many ancient temples on the Golden Summit, and ruins such as Huixiangping, Old Golden Summit, and Yuantong Hall can still be found in several locations.
3.6 The Imperially Bestowed Stele of Mount Fanjing
The Imperially Bestowed Stele, fully titled Stele Inscribed with the Preface to the Reconstruction of the Golden Summit of Mount Fanjing by Imperial Bestowal, was established by the decree of Emperor Wanli of the Ming Dynasty. It is located below the Old Golden Summit of Mount Fanjing. The stele stands 2.9 meters tall, with a central inscription panel measuring 1.85 meters in height and 1.51 meters in width. The stele’s top is vertically inscribed with the two large characters "敕赐" (Imperially Bestowed), flanked by decorative patterns of coiling dragons and crowned with colorful clouds. The inscription is entirely in regular script, totaling 1,349 characters, including an 838-character preface and a 516-character supplementary text. The stele is simple, robust, and dignified, with vigorous and powerful calligraphy. The inscription details the religious status of Mount Fanjing at the time, the construction of its temples, and the imperial court’s recognition and bestowal upon it. It serves as a precious physical artifact for studying the historical culture, religious heritage, and the relationship between ancient politics and religion on Mount Fanjing. It bears witness to the rise and fall of Mount Fanjing as a sacred Buddhist mountain throughout history, carrying the faith and aspirations of countless monks and devotees.
Standing before the Imperially Bestowed Stele, one feels as if transported through time, witnessing the grand scenes of pilgrims flocking and temple incense flourishing. The historical information contained within the inscription unfolds like a scroll, vividly depicting the social customs, religious beliefs, and cultural atmosphere of that era. It is not merely a cold stone tablet but the core carrier of Mount Fanjing’s historical culture, an important link connecting the past and the present. Every visitor who comes to pay homage pauses before it, listening with reverence to the echoes of history and feeling the profound cultural heritage and unique historical charm of Mount Fanjing. This deepens their respect and affection for this land.
3.7 Maitreya Bodhisattva
Since the Ming and Qing dynasties, legends of Maitreya and Mount Fanjing have been widely circulated among the local people. Ancient people built the Sakyamuni and Maitreya Halls atop the peak of the New Golden Summit, symbolizing the highest Buddhist significance of Mount Fanjing. The Ming Dynasty Imperially Bestowed Stele contains specific records about Maitreya and Mount Fanjing, referring to the mountain as the "boundless Dharma realm, the palace of ultimate bliss." The Maitreya Bodhimanda on Mount Fanjing is corroborated by miraculous natural landscapes. Near the New and Old Golden Summits, one can often witness wondrous "Buddha's Halo" and "mirages," which ancient people believed were manifestations of Maitreya. Viewed from the "Buddha Worship Platform" on the ancient pilgrimage path from the western route, Mount Fanjing presents the image of three Maitreya statues standing side by side: the Old Golden Summit resembles a seated Maitreya, the New Golden Summit resembles a golden monkey paying homage to Maitreya, and the three main peaks connected together form a reclining Maitreya statue stretching over ten thousand meters.
4. Cultural Resources
4.1 Changes in Name
Mount Fanjing was first officially recorded in historical texts during the Han Dynasty. The Book of Han: Treatise on Geography referred to it as "Three Mountain Valleys." The Northern Wei text Commentary on the Water Classic continued to use this name. The Tang Dynasty Yuanhe Commandery and County Gazetteer renamed it "Chen Mountain." The Song Dynasty Universal Geography of the Taiping Era called it "Siqiong Mountain," during which time Buddhism was introduced to Mount Fanjing. By the early Ming Dynasty, Mount Fanjing had already become a famous Buddhist mountain, known by several names simultaneously: "Nine Dragon Mountain," "Rice Steamer Mountain," "Fanjing Mountain," and "Great Buddha Mountain." In the Qing Dynasty, it was referred to as "Moon Mirror Mountain" and "Zhuo Mountain."
4.2 Buddhist Culture
Mount Fanjing is a cultural mountain in southwestern China with a history of over 2,000 years. As early as the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods, Mount Fanjing belonged to the "Qianzhong Territory" of the Chu State. During the Qin Dynasty, it was part of "Qianzhong Commandery," and in the Han Dynasty, it fell under "Wuling Commandery." It has since remained a sacred mountain revered by the "Wuling Barbarians."
Buddhism on Mount Fanjing began in the Tang Dynasty and flourished during the Ming Dynasty. The Imperially Bestowed Stele erected during the Wanli reign of the Ming Dynasty praised Mount Fanjing as "standing firm between heaven and earth, unrivaled across ancient and modern times," calling it the "ancestor of all famous mountains under heaven."
In the early Ming Dynasty, the Ming government mined cinnabar and gold in the Mount Fanjing area, dispatching officials to oversee the operations. Due to the mountain’s mystical landscapes, Buddhism thrived, making it a "pure land of Brahma" aspired to by monks. Thus, it was officially named "Fanjing Mountain," while locally it was called "Great Buddha Mountain." In addition to the reconstruction of the Xiyan Temple in the early Ming Dynasty, temples such as the Tianma Temple were also built.
By the Wanli period of the Ming Dynasty, two hundred years later, Mount Fanjing was renowned as an "ancient famous mountain" due to its "Ancient Buddha Bodhimanda." Guo Zizhang, the Governor of Guizhou (a native of present-day Jiangxi Province), wrote in his Records of Guizhou (1608): "Among the mountains of Guizhou, Fanjing Mountain is the foremost, comparable to Tiantai." Xie Guogeng, a late Ming poet from Zhejiang who retreated to Mount Fanjing after failing in his resistance against the Qing, even styled himself "the Hermit of Tiantai."














Comments
Post a Comment