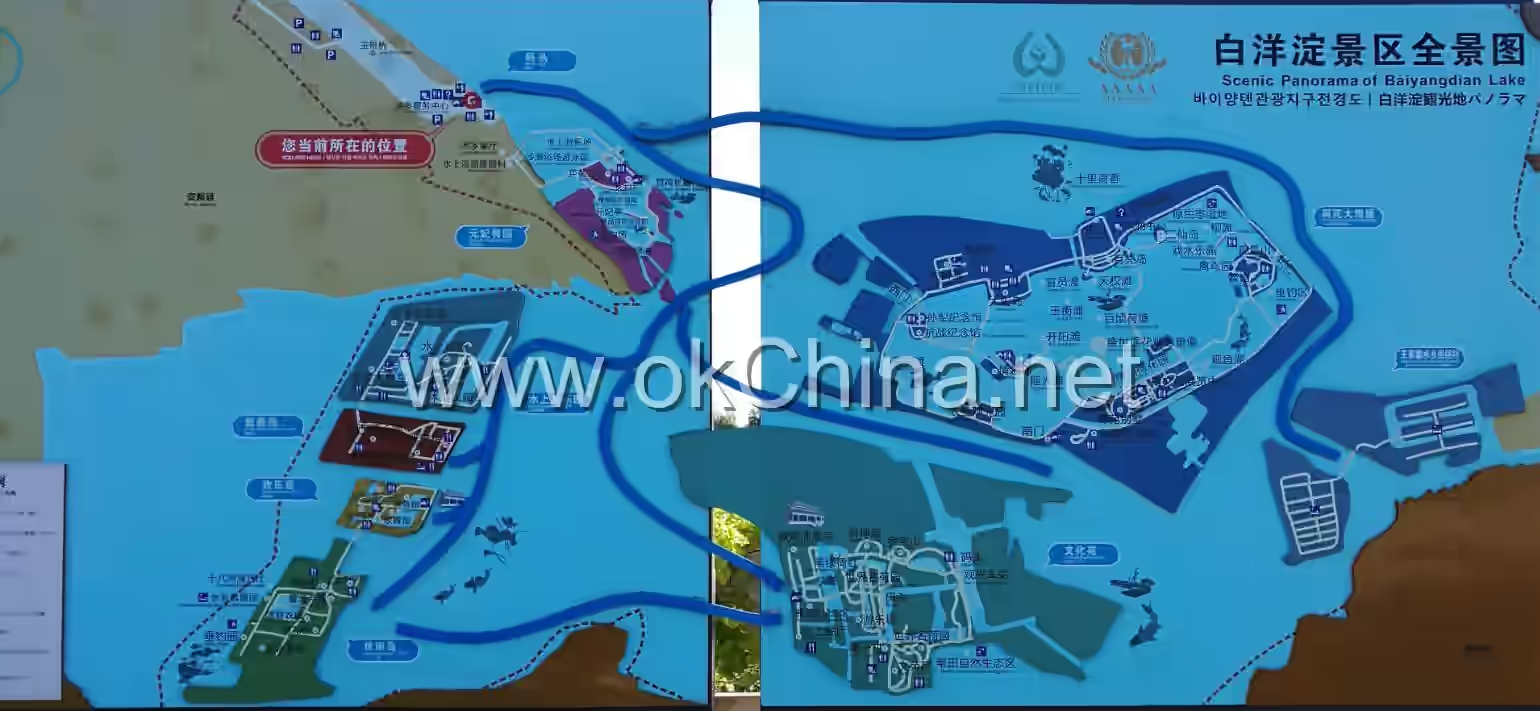
Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area in Baoding
I. Introduction
The Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area in Baoding is the largest inland lake in Hebei Province, covering a total area of 366 square kilometers. Located in the central part of Hebei Province, it lies in the heart of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, approximately 189 kilometers south of Shijiazhuang, 162 kilometers north of Beijing, and 155 kilometers east of Tianjin.
Historically, Baiyangdian served as a contested border between the Yan and Zhao states during the Warring States period and later between the Song and Liao dynasties. Before the Republic of China era, Baiyangdian was an important waterway connecting Baoding and Tianjin. The traditional industries in the lake area were fishing and reed production. After the 20th century, with the rise of domestic tourism in China, it gradually became a tourist destination. In 2007, it was designated as a National 5A Tourist Attraction. It is renowned as a place that "earns a fortune daily" and is "autumn-like all year round." It has been poetically praised as the "Jiangnan of the North" and celebrated as the "Land of Fish and Rice." Former President Jiang Zemin personally inscribed the words: "Baiyangdian, the Pearl of North China."
II. Geographical Environment
Location and Territory
Baiyangdian holds a historical and geographical significance as the "confluence of nine rivers flowing into the sea." The Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area in Baoding is situated within Anxin County of the Xiong'an New Area, approximately 150 kilometers from Beijing and Tianjin, and about 30 kilometers from downtown Baoding. The lake is surrounded by counties such as Anxin, Xiongxian, Rongcheng, Gaoyang, and Renqiu, with 85% of the lake area located within Anxin County.
Hydrology
The upstream rivers of Baiyangdian include the Tang River, Fu River, Cao River, Ping River, Bao River, Qingshui River, Zhulong River, Xiaoyi River, and Jinxian River, collectively known as the "Nine Rivers' Confluence."
Topography and Landforms
The Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area is located in a low-lying area between the alluvial fans of the Yongding River and the Hutuo River at the eastern foothills of the Taihang Mountains. It is one of the larger perennial lakes on the North China Plain. Rivers flow from west to east and south to north, forming a fan-shaped river network that converges into a natural depression.
The lake area consists of 143 lakes and marshes of varying sizes, such as Baiyangdian, Mapengdian, Shaochedian, and Zaozhadian, along with over 3,700 ditches. This creates a unique landscape where lakes are nested within lakes, ditches are interconnected, and farmland and water surfaces are interspersed.
The topography and landforms of the Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area were formed through repeated evolution from sea to lake and lake to land. Baiyangdian’s water system is unique, differing from the inland lakes of southern China and the artificial reservoirs of northern China. It is not a single vast expanse of water but a network of lakes and marshes connected by multiple rivers, forming a layout where rivers and lakes are intertwined, reed marshes and lotus ponds are scattered, and individual lakes are both separated and connected.
Climate Type
The Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area experiences a temperate continental monsoon climate, characterized by distinct seasons. Spring is dry and windy, summer is hot and rainy, autumn is clear and pleasant, and winter is cold with little snow.
The average annual temperature is 12.1°C, with 2,638.3 hours of sunshine and a frost-free period of 203 days. The average annual precipitation is 552.7 mm.
III. Natural Resources
Animals
The Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area is home to 14 species of mammals, belonging to 5 orders, 8 families, and 12 genera. All are nationally protected terrestrial wildlife species with beneficial, economic, or scientific value.
The area hosts 197 species of birds, including 78 summer migrants, 19 resident birds, 88 passage migrants, and 7 winter migrants. Among them, four species are nationally protected Class I birds: the Red-crowned Crane, Siberian Crane, Great Bustard, and Oriental White Stork. Additionally, 26 species are nationally protected Class II birds, including the Eurasian Spoonbill, Greater White-fronted Goose, Demoiselle Crane, Common Crane, Whooper Swan, Pied Harrier, and Long-eared Owl.
The area is rich in fish resources, with 54 species, primarily carp, snakehead, and yellow catfish. The Cyprinidae family is the most diverse, comprising 30 genera and 34 species.
Furthermore, common benthic animals in the area include arthropods, mollusks, and annelids, totaling 38 species. The dominant groups are mollusks and crustaceans, with river snails being the most abundant.
Plants
The Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area features 47 species of large aquatic plants, including 21 emergent plants, 7 floating-leaved plants, 4 free-floating plants, and 15 submerged plants. The vast water area has formed aquatic plant communities dominated by lotus, reeds, foxnuts, and water chestnuts.
Terrestrial plants are mainly broad-leaved tree species. Common woody plants include poplar, willow, locust, and apple trees. Herbaceous plants are primarily from the Asteraceae and Fabaceae families. Crops include wheat, corn, rice, sorghum, and soybeans.
Algae in the area belong to 9 phyla, 11 classes, 26 orders, 55 families, 142 genera, 406 species, and 27 varieties. Dominant families include Desmidiaceae, Naviculaceae, and Chroococcaceae, comprising 70 genera and 292 species.
IV. Main Attractions
Yuanfei Lotus Garden
Yuanfei Lotus Garden is located south of the Anxin County Tourist Pier. Built in 2001, it covers approximately 1,800 acres and is themed around natural ecology. The garden is divided into six themed areas: a beach bathing area, lotus viewing area, red tourism area, reed maze area, water recreation area, and dining and accommodation area.
Yuanfei Lotus Garden was where Li Shi’er, the imperial consort of Emperor Zhangzong of the Jin Dynasty, enjoyed lotus flowers. To allow the consort to see lotus flowers while dressing in the morning, Emperor Zhangzong built a lotus garden here, along with a dressing table, later known as the "Consort’s Dressing Table." When developing this attraction, it was named "Yuanfei Lotus Garden."
Grand Lotus Garden
The Baiyangdian Grand Lotus Garden is situated within the Baiyangdian Scenic Area in Anxin County, Hebei Province. Covering over 2,000 acres, with a water area of 1,560 acres, it features 699 varieties of lotus from China and abroad. The flowers come in colors such as red, yellow, white, pink, and light green, with single, double, and multi-layered petals. The plants range from small bowl lotuses suitable for tabletops to large South American Victoria water lilies capable of bearing dozens of pounds.
The Grand Lotus Garden includes five zones (welcome zone, service zone, dining zone, lotus-picking zone, and viewing zone), four gardens (premium lotus garden, tranquil garden, fishing garden, and folk culture garden), three ports (boat docking port, fish viewing port, and leisure port), two beaches (beach bathing area and leisure beach), and one hill (viewing hill).
The garden features a ten-mile circular road, a hundred-acre lotus pond, a thousand-foot flower-viewing bridge, and a ten-thousand-meter boat channel.
Mandarin Duck Island
Mandarin Duck Island is located within the Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area, covering 64,000 square meters. Visitors can watch scheduled performances of cormorant fishing, water town wedding customs, and Baiyangdian folk customs on the island.
The Baiyangdian Window on the island was transformed from the original "Water Margin Liangshan Palace." Located on the south side of Mandarin Duck Island, it covers 5,000 square meters and includes "six halls and one garden": the introduction hall, cultural history hall, folk customs hall, natural resources hall, heroic epic hall, glorious achievements hall, and water town风情园. It focuses on showcasing Baiyangdian’s wetland natural culture, traditional historical culture, and folk culture. The natural culture highlights the formation and changes of Baiyangdian, the historical culture emphasizes the famous Yanling Brigade and the character Zhang Ga from "Little Soldier Zhang Ga," and the folk culture showcases the local customs of Baiyangdian.
Leisure Island
Leisure Island is located south of Mandarin Duck Island. Built on May 1, 2002, it covers over 200 acres and is themed around dining, accommodation, entertainment, and folk customs. The eastern side of the island is a revolutionary history exhibition area, focusing on the establishment of the Yanling Brigade and the life stories of Zhao Bo, the原型 of the character Zhang Ga in "Little Soldier Zhang Ga," including photos of him meeting national leaders.
Leisure Island is also a culinary destination, featuring特色休闲屋 and a folk-style fishing village. It offers entertainment activities such as swimming, boating,八卦迷宫, fishing, duck competitions, karaoke, and cormorant fishing performances.
Exotic Customs Garden
The Baiyangdian Exotic Customs Garden is located within the Anxin Baiyangdian Scenic Area, north of Mandarin Duck Island and south of Leisure Island. Covering 30 acres, it is an entertainment park featuring high-altitude达瓦孜 performances, Thai boxing, Thai folk歌舞, European女子摔跤, crocodile shows, African lion hunting, mysterious小屋 with倒流 water, and攀岩弹跳.
In 2007, the Exotic Customs Garden was upgraded, adding over ten entertainment projects such as bumper cars, pirate ships, laser shooting,水上步行球, and宇宙大翻转.
Baodao Water Amusement Park
Baodao Water Amusement Park was built in 2008, located north of Mandarin Duck Island, covering 85,800 square meters.
The main entertainment projects at Baodao Water Amusement Park include Belarusian water ballet, Thai红艺人 performances, Guinness-record高空飞车, skilled equestrian shows, animal training, and acrobatics. The island’s activities combine entertainment,观赏, and竞技娱乐.
Baiyangdian Cultural Park
Baiyangdian Cultural Park is located within Baiyangdian, covering approximately 2,000 acres. Its themes encompass four cultural aspects: history, tradition, folk customs, and ecology.
The park features eight major景观: Kangxi’s Water Hunting Palace, Pei’en Temple, Qianping, East堤烟柳, West淀风荷, Aquatic植物园, Reed Flower Village Resort, and Yanling Brigade Memorial Hall.### Baiyangdian Fishermen's Paradise
Baiyangdian Fishermen's Paradise was established in 2001, covering an area of over 10,000 mu. Historically known as Shaoche Dian, this site was an ancient battlefield where the famous Song Dynasty general Yang Yanzhao resisted the Jin and Liao forces. The scenic area features vast, clear waters and is a typical wetland sightseeing destination.
Wangjiazhai Folk Village
Wangjiazhai Folk Village covers an area of 4,995 square meters and serves as a resort base for experiencing Baiyangdian's folk customs. Here, visitors can engage in activities such as fishing, catching shrimp, training cormorants, boating, and preparing water-town cuisine, immersing themselves in the pastoral life of fishermen in this northern water town.
V. History and Culture
Historical Evolution
Ancient Times
During the Neolithic Age, human activities were already present in the western and southern parts of the Dian area (present-day Liucun and Liangzhuang in Anxin County). The ancient Yellow River consistently flowed through the Hebei Plain, with the Baiyangdian region being a crucial passage. Its route followed the eastern flow of the alluvial fan of the Taihang Mountains into the sea, providing a reliable water source for the Baiyangdian area. Archaeological data indicate that the lakes and marshes in Baiyangdian were relatively scattered during that period, unlike the vast interconnected water bodies seen today.
During the Western Jin Dynasty, the Baiyangdian basin transitioned from dry to water-rich conditions, giving rise to numerous shifting lakes and marshes. The poet and writer Zuo Si (250–305 AD) wrote in his "Ode to the Wei Capital": "The lake where carps are dug, the deep pool where reeds grow." The Tang Dynasty scholar Li Shan annotated that "the lake where carps are dug" was located west of Moxian in Hejian (Moxian refers to Mozhou in Renqiu County), a location entirely consistent with Baiyangdian's position. The name "Dian" (lake/marsh) originated from this.
During the Song-Liao confrontation, the two sides used the Baigou line as their boundary. To defend against Liao incursions, the Song Dynasty established numerous ponds and marshes along the route from present-day Baoding to Anxin, Xiong County, Bazhou, and as far as Qing County, forming a complete defensive line of ponds and marshes. This created a "Water Great Wall" composed of river networks, trenches, paddy fields, and lakes. The "Song History: Treatise on Rivers and Canals" records names such as "Baiyang Dian," "Bianwu Dian," and "Lao Dian." "Baiyang Dian" is today's Baiyangdian, marking the first appearance of "Baiyang Dian" as a place name in historical records. As for why it was written as "sheep" (羊), some believe that Baiyangdian's waters were vast and turbulent at the time, with strong winds whipping up waves resembling running sheep, hence the name.
During the Ming Dynasty's Zhengde era, Baiyangdian regained its water, presenting a landscape described as "vast and boundless, stretching to the horizon." In the Qing Dynasty, Baiyangdian frequently suffered from floods. Emperors Shunzhi and Kangxi prioritized its management, constructing numerous embankments, sluices, and culverts. County records note that "the embankments stretched蜿蜒 for hundreds of miles." In the 18th year of Kangxi's reign (1679), Emperor Kangxi visited Baiyangdian and, inspired by its expansive waters, composed the poem "Baiyang Lake": "Gazing afar at Baiyang's waters, sails set off among distant trees. The flow is calm, waves unmoving, emerald hues fill the lake." Baiyangdian thus became a picturesque and enchanting landscape. During his 61-year reign, Kangxi visited Baiyangdian 40 times, participated in 29 water hunts, and established four temporary palaces.
Modern Era
On April 1, 2017, the Xiong'an New Area was officially established, with most of Baiyangdian falling under its jurisdiction. In January 2019, following the establishment of the Xiong'an New Area, the "Baiyangdian Ecological Environment Governance and Protection Plan (2018–2035)" was formulated. From a watershed management perspective, focusing on water quality and ecological restoration goals, comprehensive measures such as water replenishment, pollution control, dredging, and relocation were implemented to fully restore Baiyangdian's function as the "Kidney of North China." In April 2018, free Wi-Fi was officially launched in the Baiyangdian scenic area. In early 2019, the Xiong'an New Area implemented integrated management of sewage, garbage, and toilets in villages within and around the Dian. In 2022, the Xiong'an New Area designated nine important bird habitats within Baiyangdian. On April 16, 2023, the Baiyangdian scenic area officially began operations. From October 15, 2023, to March 30, 2024, to maintain the image of Baiyangdian as a 5A-level scenic area and ensure the safety of visitors' lives and property, the scenic area was closed to tourists for winter management, prioritizing visitor responsibility and safety. On April 20, 2024, the Baiyangdian scenic area began trial operations, with official reopening scheduled for May 1.
Red Culture
During the War of Resistance Against Japan, the anti-Japanese armed force "Yanling Team," active in Baiyangdian, utilized the favorable terrain of widespread reed marshes and交错 waterways under the leadership of the Communist Party of China. They employed flexible guerrilla tactics to achieve victory against stronger foes, dealing heavy blows to the Japanese invaders, boosting the morale of the Chinese nation, and demonstrating the wisdom and courage of the people of Yan and Zhao.
Inscriptions by Celebrities
On September 18, 1991, Comrade Jiang Zemin inspected Baiyangdian and inscribed the words: "Baiyangdian, the Pearl of North China." In 2001, Comrade Qian Qichen visited Baiyangdian and inscribed: "Northern Water Town, Red Lotuses and Green Reeds."
Folk Legends
Long ago, on a Mid-Autumn night, the fairy Chang'e stole the elixir of immortality and, against her will, drifted away from the Moon Palace. Just as she was about to descend to the mortal world, she suddenly awoke with a start. In her alarm, her precious mirror fell to the earth, shattering into 143 pieces of varying sizes, forming 143 lakes and marshes.






















Comments
Post a Comment